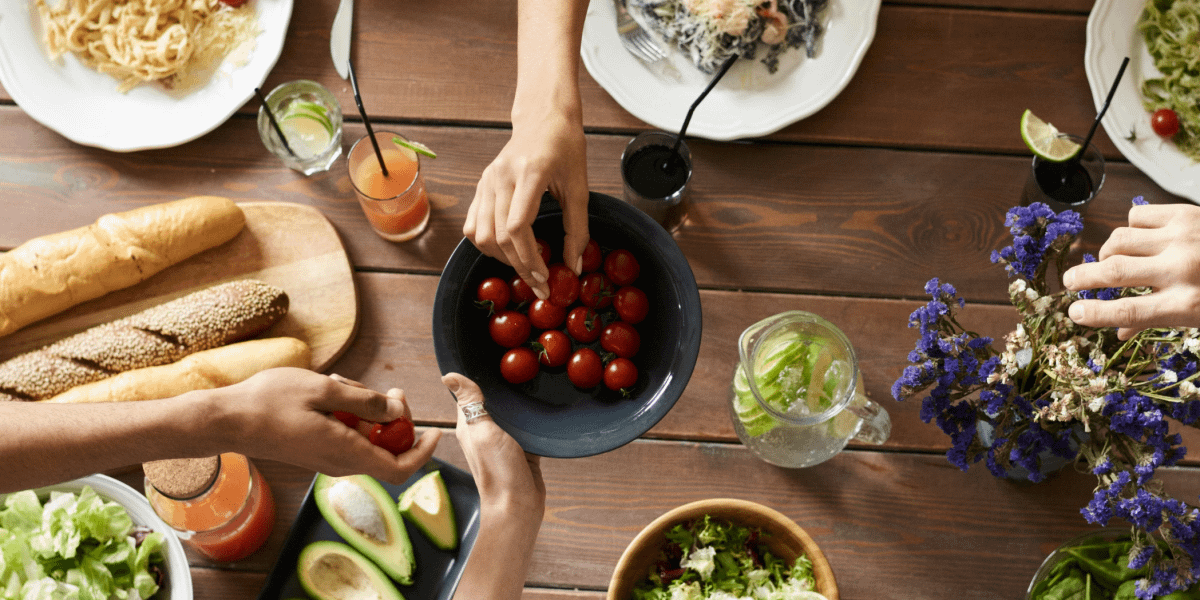
The saying “you are what you eat” holds more truth than many realize. Food isn’t just fuel for the body; it can be a powerful tool for promoting health and preventing disease. The concept of “food as medicine” has been embraced for centuries in various cultures, and modern science continues to uncover the profound impact that diet has on our overall well-being. By understanding how different foods can support your body, you can make choices that nourish your health from the inside out.
The Healing Power of Nutrients
Our bodies require a variety of nutrients to function optimally—vitamins, minerals, antioxidants, fiber, and healthy fats all play crucial roles in maintaining health. These nutrients are not just building blocks; they actively contribute to preventing and managing a wide range of health conditions.
- Vitamins and Minerals: Essential for countless biochemical processes, vitamins like A, C, D, and E, along with minerals like magnesium, calcium, and zinc, support immune function, bone health, energy production, and more. For example, vitamin C is a potent antioxidant that helps protect cells from damage and supports the immune system.
- Antioxidants: Found in fruits, vegetables, and certain whole grains, antioxidants help neutralize harmful free radicals in the body, reducing oxidative stress and lowering the risk of chronic diseases such as heart disease, cancer, and neurodegenerative disorders.
- Fiber: Dietary fiber, found in plant-based foods like fruits, vegetables, legumes, and whole grains, is crucial for digestive health. It helps regulate blood sugar levels, lowers cholesterol, and supports a healthy gut microbiome, which is linked to improved immunity and mental health.
- Healthy Fats: Omega-3 fatty acids, found in fish, nuts, and seeds, have anti-inflammatory properties and support heart health, brain function, and joint mobility. Healthy fats are also vital for absorbing fat-soluble vitamins like A, D, E, and K.
Food as Preventative Medicine
Incorporating a variety of nutrient-dense foods into your diet can help prevent and manage numerous health conditions:
- Heart Disease: A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and healthy fats can significantly reduce the risk of heart disease. Foods like leafy greens, berries, nuts, and fatty fish are particularly beneficial for heart health due to their high content of heart-healthy nutrients like fiber, antioxidants, and omega-3 fatty acids.
- Diabetes: Managing blood sugar levels is crucial for preventing and managing diabetes. Consuming whole grains, legumes, and fiber-rich vegetables helps regulate blood sugar, while reducing intake of refined sugars and processed foods can prevent insulin resistance.
- Cancer Prevention: Certain foods have been linked to a lower risk of cancer, thanks to their rich content of antioxidants and anti-inflammatory compounds. Cruciferous vegetables like broccoli and kale, as well as fruits like berries and tomatoes, contain compounds that may help protect against cancer by reducing oxidative damage and inflammation.
- Mental Health: Emerging research suggests that diet plays a significant role in mental health. Foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids, antioxidants, and vitamins like B12 and folate are associated with better mood regulation and a lower risk of depression and anxiety.
Food as Medicine in Everyday Life
Adopting the “food as medicine” approach doesn’t mean making drastic changes overnight. It’s about making small, sustainable adjustments to your diet that can have a big impact over time.
- Incorporate More Plants: Aim to fill half your plate with fruits and vegetables at every meal. These foods are packed with vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants that support overall health.
- Choose Whole Grains: Replace refined grains with whole grains like quinoa, brown rice, and oats. Whole grains are higher in fiber and nutrients, which help regulate blood sugar and support digestive health.
- Prioritize Healthy Fats: Include sources of healthy fats, such as avocados, nuts, seeds, and olive oil, in your diet. These fats support heart health and help reduce inflammation.
- Reduce Processed Foods: Limit the consumption of highly processed foods that are often high in unhealthy fats, sugars, and sodium. Instead, focus on whole, minimally processed foods that provide more nutrients and less empty calories.
- Stay Hydrated: Water is essential for every function in the body, from digestion to detoxification. Herbal teas and water-rich foods like cucumbers and watermelon can also contribute to your daily hydration.
The Connection Between Food and Gut Health
The gut microbiome, a complex community of microorganisms in the digestive tract, plays a crucial role in health. A diverse and balanced microbiome is linked to improved digestion, immunity, and even mental health. What you eat directly influences the composition and health of your gut microbiome.
- Probiotic-Rich Foods: Fermented foods like yogurt, kefir, sauerkraut, and kimchi contain beneficial bacteria that can support a healthy gut microbiome.
- Prebiotic Foods: Foods high in prebiotic fibers, such as garlic, onions, leeks, and bananas, feed the beneficial bacteria in your gut, helping them thrive.
- Diverse Diet: Eating a variety of plant-based foods ensures that your gut bacteria receive a wide range of nutrients, promoting a diverse and healthy microbiome.
Conclusion
The idea of food as medicine is a powerful reminder that what we eat plays a central role in our health. By choosing nutrient-rich, whole foods and making mindful decisions about our diet, we can support our bodies in healing, thriving, and preventing disease. Remember, the journey to better health through food is not about perfection but about making better choices, one meal at a time.
4o